Below interview questions are contributed by ASIC_diehard (Thanks a lot !). Below questions are asked for senior position in Physical Design domain. The questions are also related to Static Timing Analysis and Synthesis. Answers to some questions are given as link. Remaining questions will be answered in coming blogs.
Common introductory questions every interviewer asks are:
- Discuss about the projects worked in the previous company.
- What are physical design flows, various activities you are involved?
- Design complexity, capacity, frequency, process technologies, block size you handled.
Intel
- Why power stripes routed in the top metal layers?
The resistivity of top metal layers are less and hence less IR drop is seen in power distribution network. If power stripes are routed in lower metal layers this will use good amount of lower routing resources and therefore it can create routing congestion.
- Why do you use alternate routing approach HVH/VHV (Horizontal-Vertical-Horizontal/ Vertical-Horizontal-Vertical)?
Answer:
This approach allows routability of the design and better usage of routing resources.
- What are several factors to improve propagation delay of standard cell?
Answer:
Improve the input transition to the cell under consideration by up sizing the driver.
Reduce the load seen by the cell under consideration, either by placement refinement or buffering.
If allowed increase the drive strength or replace with LVT (low threshold voltage) cell.
- How do you compute net delay (interconnect delay) / decode RC values present in tech file?
- What are various ways of timing optimization in synthesis tools?
Answer:
Logic optimization: buffer sizing, cell sizing, level adjustment, dummy buffering etc.
Less number of logics between Flip Flops speedup the design.
Optimize drive strength of the cell , so it is capable of driving more load and hence reducing the cell delay.
Better selection of design ware component (select timing optimized design ware components).
Use LVT (Low threshold voltage) and SVT (standard threshold voltage) cells if allowed.
- What would you do in order to not use certain cells from the library?
Answer:
Set don’t use attribute on those library cells.
- How delays are characterized using WLM (Wire Load Model)?
Answer:
For a given wireload model the delay are estimated based on the number of fanout of the cell driving the net.
Fanout vs net length is tabulated in WLMs.
Values of unit resistance R and unit capacitance C are given in technology file.
Net length varies based on the fanout number.
Once the net length is known delay can be calculated; Sometimes it is again tabulated.
- What are various techniques to resolve congestion/noise?
Answer:
Routing and placement congestion all depend upon the connectivity in the netlist , a better floor plan can reduce the congestion.
Noise can be reduced by optimizing the overlap of nets in the design.
- Let’s say there enough routing resources available, timing is fine, can you increase clock buffers in clock network? If so will there be any impact on other parameters?
Answer:
No. You should not increase clock buffers in the clock network. Increase in clock buffers cause more area , more power. When everything is fine why you want to touch clock tree??
- How do you optimize skew/insertion delays in CTS (Clock Tree Synthesis)?
Answer:
Better skew targets and insertion delay values provided while building the clocks.
Choose appropriate tree structure – either based on clock buffers or clock inverters or mix of clock buffers or clock inverters.
For multi clock domain, group the clocks while building the clock tree so that skew is balanced across the clocks. (Inter clock skew analysis).
- What are pros/cons of latch/FF (Flip Flop)?
Answer: Pros and cons of latch and flip flop
- How you go about fixing timing violations for latch- latch paths?
- As an engineer, let’s say your manager comes to you and asks for next project die size estimation/projection, giving data on RTL size, performance requirements. How do you go about the figuring out and come up with die size considering physical aspects?
- How will you design inserting voltage island scheme between macro pins crossing core and are at different power wells? What is the optimal resource solution?
- What are various formal verification issues you faced and how did you resolve?
- How do you calculate maximum frequency given setup, hold, clock and clock skew?
- What are effects of metastability?
Answer: Metastability
- Consider a timing path crossing from fast clock domain to slow clock domain. How do you design synchronizer circuit without knowing the source clock frequency?
- How to solve cross clock timing path?
- How to determine the depth of FIFO/ size of the FIFO?
Answer: FIFO Depth
STmicroelectronics
- What are the challenges you faced in place and route, FV (Formal Verification), ECO (Engineering Change Order) areas?
- How long the design cycle for your designs?
- What part are your areas of interest in physical design?
- Explain ECO (Engineering Change Order) methodology.
- Explain CTS (Clock Tree Synthesis) flow.
Answer: Clock Tree Synthesis
- What kind of routing issues you faced?
- How does STA (Static Timing Analysis) in OCV (On Chip Variation) conditions done? How do you set OCV (On Chip Variation) in IC compiler? How is timing correlation done before and after place and route?
Answer: Process-Voltage-Temperature (PVT) Variations and Static Timing Analysis (STA)
- If there are too many pins of the logic cells in one place within core, what kind of issues would you face and how will you resolve?
- Define hash/ @array in perl.
- Using TCL (Tool Command Language, Tickle) how do you set variables?
- What is ICC (IC Compiler) command for setting derate factor/ command to perform physical synthesis?
- What are nanoroute options for search and repair?
- What were your design skew/insertion delay targets?
- How is IR drop analysis done? What are various statistics available in reports?
- Explain pin density/ cell density issues, hotspots?
- How will you relate routing grid with manufacturing grid and judge if the routing grid is set correctly?
- What is the command for setting multi cycle path?
- If hold violation exists in design, is it OK to sign off design? If not, why?
Texas Instruments (TI)
- How are timing constraints developed?
- Explain timing closure flow/methodology/issues/fixes.
- Explain SDF (Standard Delay Format) back annotation/ SPEF (Standard Parasitic Exchange Format) timing correlation flow.
- Given a timing path in multi-mode multi-corner, how is STA (Static Timing Analysis) performed in order to meet timing in both modes and corners, how are PVT (Process-Voltage-Temperature)/derate factors decided and set in the Primetime flow?
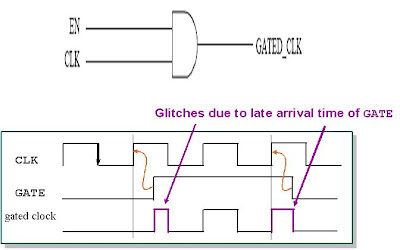
- With respect to clock gate, what are various issues you faced at various stages in the physical design flow?
- What are synthesis strategies to optimize timing?
- Explain ECO (Engineering Change Order) implementation flow. Given post routed database and functional fixes, how will you take it to implement ECO (Engineering Change Order) and what physical and functional checks you need to perform?
Qualcomm
- In building the timing constraints, do you need to constrain all IO (Input-Output) ports?
- Can a single port have multi-clocked? How do you set delays for such ports?
- How is scan DEF (Design Exchange Format) generated?
- What is purpose of lockup latch in scan chain?
- Explain short circuit current.
Answer: Short Circuit Power
- What are pros/cons of using low Vt, high Vt cells?
Answer:
Multi Threshold Voltage Technique
Issues With Multi Height Cell Placement in Multi Vt Flow
- How do you set inter clock uncertainty?
Answer:
set_clock_uncertainty –from clock1 -to clock2
- In DC (Design Compiler), how do you constrain clocks, IO (Input-Output) ports, maxcap, max tran?
- What are differences in clock constraints from pre CTS (Clock Tree Synthesis) to post CTS (Clock Tree Synthesis)?
Answer:
Difference in clock uncertainty values; Clocks are propagated in post CTS.
In post CTS clock latency constraint is modified to model clock jitter.
- How is clock gating done?
Answer: Clock Gating
- What constraints you add in CTS (Clock Tree Synthesis) for clock gates?
Answer:
Make the clock gating cells as through pins.
- What is trade off between dynamic power (current) and leakage power (current)?
Answer:
Leakage Power Trends
Dynamic Power
- How do you reduce standby (leakage) power?
Answer: Low Power Design Techniques
- Explain top level pin placement flow? What are parameters to decide?
- Given block level netlists, timing constraints, libraries, macro LEFs (Layout Exchange Format/Library Exchange Format), how will you start floor planning?
- With net length of 1000um how will you compute RC values, using equations/tech file info?
- What do noise reports represent?
- What does glitch reports contain?
- What are CTS (Clock Tree Synthesis) steps in IC compiler?
- What do clock constraints file contain?
- How to analyze clock tree reports?
- What do IR drop Voltagestorm reports represent?
- Where /when do you use DCAP (Decoupling Capacitor) cells?
- What are various power reduction techniques?
Answer: Low Power Design Techniques
Hughes Networks
- What is setup/hold? What are setup and hold time impacts on timing? How will you fix setup and hold violations?
- Explain function of Muxed FF (Multiplexed Flip Flop) /scan FF (Scal Flip Flop).
- What are tested in DFT (Design for Testability)?
- In equivalence checking, how do you handle scanen signal?
- In terms of CMOS (Complimentary Metal Oxide Semiconductor), explain physical parameters that affect the propagation delay?
- What are power dissipation components? How do you reduce them?
Answer:
Short Circuit Power
Leakage Power Trends
Dynamic Power
Low Power Design Techniques
- How delay affected by PVT (Process-Voltage-Temperature)?
Answer: Process-Voltage-Temperature (PVT) Variations and Static Timing Analysis (STA)
- Why is power signal routed in top metal layers?
Avago Technologies (former HP group)
- How do you minimize clock skew/ balance clock tree?
- Given 11 minterms and asked to derive the logic function.
- Given C1= 10pf, C2=1pf connected in series with a switch in between, at t=0 switch is open and one end having 5v and other end zero voltage; compute the voltage across C2 when the switch is closed?
- Explain the modes of operation of CMOS (Complimentary Metal Oxide Semiconductor) inverter? Show IO (Input-Output) characteristics curve.
- Implement a ring oscillator.
- How to slow down ring oscillator?
Hynix Semiconductor
- How do you optimize power at various stages in the physical design flow?
- What timing optimization strategies you employ in pre-layout /post-layout stages?
- What are process technology challenges in physical design?
- Design divide by 2, divide by 3, and divide by 1.5 counters. Draw timing diagrams.
- What are multi-cycle paths, false paths? How to resolve multi-cycle and false paths?
- Given a flop to flop path with combo delay in between and output of the second flop fed back to combo logic. Which path is fastest path to have hold violation and how will you resolve?
- What are RTL (Register Transfer Level) coding styles to adapt to yield optimal backend design?
- Draw timing diagrams to represent the propagation delay, set up, hold, recovery, removal, minimum pulse width.
About Contributor
ASIC_diehard has more than 5 years of experience in physical design, timing, netlist to GDS flows of Integrated Circuit development. ASIC_diehard's fields of interest are backend design, place and route, timing closure, process technologies.
Readers are encouraged to discuss answers to these questions. Just click on the 'post a comment' option below and put your comments there. Alternatively you can send your answers/discussions to my mail id: shavakmm@gmail.com
Creating the reference libraries There are two reference libraries required. One is low Vt cell library and another is high Vt cell library. These libraries have two different height cells. Reference libraries are created as per the standard synopsys flow. Library creation flow is given in Figure 1. Read_lib command is used for this purpose. As TF and LEF files are available TF+LEF option is chosen for library creation. After the completion of the physical library preparation steps, logical libraries are prepared.
Figure 1 Library preparation command window
Different Unit Tile Creation
The unit tile height of lvt cells is 2.52 µ and hvt cells are 1.96 µ. Hence two separate unit tiles have to be created and should be added in the technology file. Hvt reference library is created with the unit tile name “unit” and lvt reference library is created with unit tile name “lvt_unit”. By default “unit” tile is defined in technology file and the other unit tile “lvt_unit” is also added to the technology file.
Figure 2. Tile height specifications in library preparation
Floor Planning
70% of the core utilization is provided. Aspect ratio is kept at 1. Rows are flipped, double backed and made channel less. No Top Design Format (TDF) file is selected as default placement of the IO pins are considered. Since we have multi height cells in the reference library separate placement rows have to be provided for two different unit tiles. The core area is divided into two separate unit tile section providing larger area for Hvt unit tile as shown in the Figure 3.
Figure 3. Different unit tile placement
First as per the default floor planning flow rows are constructed with unit tile. Later rows are deleted from the part of the core area and new rows are inserted with the tile “lvt_unit”. Improper allotment of area can give rise to congestion. Some iteration of trial and error experiments were conducted to find best suitable area for two different unit tiles. The “unit” tile covers 44.36% of core area while “lvt_unit” 65.53% of the core area. PR summary report of the design after the floor planning stage is provided below.
PR Summary:
Number of Module Cells: 70449
Number of Pins: 368936
Number of IO Pins: 298
Number of Nets: 70858
Average Pins Per Net (Signal): 3.20281
Chip Utilization:
Total Standard Cell Area: 559367.77
Core Size: width 949.76, height 947.80; area 900182.53
Chip Size: width 999.76, height 998.64; area 998400.33
Cell/Core Ratio: 62.1394%
Cell/Chip Ratio: 56.0264%
Number of Cell Rows: 392
Placement Issues with Different Tile Rows
Legal placement of the standard cells is automatically taken care by Astro tool as two separate placement area is defined for multi heighten cells. Corresponding tile utilization summary is provided below.
PR Summary:
[Tile Utilization]
============================================================
unit 257792 114353 44.36%
lvt_unit 1071872 702425 65.53%
============================================================
But this method of placement generates unacceptable congestion around the junction area of two separate unit tile sections. The congestion map is shown in Figure 4.
Figure 4. Congestion
There are two congestion maps. One is related to the floor planning with aspect ratio 1 and core utilization of 70%. This shows horizontal congestion over the limited value of one all over the core area meaning that design can’t be routed at all. Hence core area has to be increased by specifying height and width. The other congestion map is generated with the floor plan wherein core area is set to 950 µm. Here we can observe although congestion has reduced over the core area it is still a concern over the area wherein two different unit tiles merge as marked by the circle. But design can be routable and can be carried to next stages of place and route flow provided timing is met in subsequent implementation steps.
Tighter timing constraints and more interrelated connections of standard cells around the junction area of different unit tiles have lead to more congestion. It is observed that increasing the area isn't a solution to congestion. In addition to congestion, situation verses with the timing optimization effort by the tool. Timing target is not able to meet. Optimization process inserts several buffers around the junction area and some of them are placed illegally due to the lack of placement area.
Corresponding timing summary is provided below:
Timing/Optimization Information:
[TIMING]
Setup Hold Num Num
Type Slack Num Total Target Slack Num Trans MaxCap Time
========================================================
A.PRE -3.491 3293 -3353.9 0.100 10000.000 0 8461 426 00:02:26
A.IPO -0.487 928 -271.5 0.100 10000.000 0 1301 29 00:01:02
A.IPO -0.454 1383 -312.8 0.100 10000.000 0 1765 36 00:01:57
A.PPO -1.405 1607 -590.9 0.100 10000.000 0 2325 32 00:00:58
A.SETUP -1.405 1517 -466.4 0.100 -0.168 6550 2221 31 00:04:10
========================================================
Since the timing is not possible to meet design has to be abandoned from subsequent steps. Hence in a multi vt design flow cell library with multi heights are not preferred.
References
[1] Astro, User Guide, Version X-2005.09, September 2005
- 1) Chip utilization depends on ___.
a. Only on standard cells
b. Standard cells and macros
c. Only on macros
d. Standard cells macros and IO pads
- 2) In Soft blockages ____ cells are placed.
a. Only sequential cells
b. No cells
c. Only Buffers and Inverters
d. Any cells
- 3) Why we have to remove scan chains before placement?
a. Because scan chains are group of flip flop
b. It does not have timing critical path
c. It is series of flip flop connected in FIFO
d. None
- 4) Delay between shortest path and longest path in the clock is called ____.
a. Useful skew
b. Local skew
c. Global skew
d. Slack
- 5) Cross talk can be avoided by ___.
a. Decreasing the spacing between the metal layers
b. Shielding the nets
c. Using lower metal
layers
d. Using long nets
- 6) Prerouting means routing of _____.
a. Clock nets
b. Signal nets
c. IO nets
d. PG nets
- 7) Which of the following metal layer has Maximum resistance?
a. Metal1
b. Metal2
c. Metal3
d. Metal4
- 8) What is the goal of CTS?
a. Minimum IR Drop
b. Minimum EM
c. Minimum Skew
d. Minimum Slack
- 9) Usually Hold is fixed ___.
a. Before Placement
b. After Placement
c. Before
CTS
d. After
CTS
- 10) To achieve better timing ____ cells are placed in the critical path.
a.
HVT
b.
LVT
c.
RVT
d.
SVT
- 11) Leakage power is inversely proportional to ___.
a. Frequency
b. Load Capacitance
c. Supply voltage
d. Threshold Voltage
- 12) Filler cells are added ___.
a. Before Placement of std cells
b. After Placement of Std Cells
c. Before
Floor planning
d. Before
Detail Routing
- 13) Search and Repair is used for ___.
a. Reducing IR Drop
b. Reducing
DRC
c. Reducing EM
violations
d. None
- 14) Maximum current density of a metal is available in ___.
a. .lib
b. .v
c. .
tf
d. .
sdc
- 15) More IR drop is due to ___.
a. Increase in metal width
b. Increase in metal length
c. Decrease in metal length
d. Lot of metal layers
- 16) The minimum height and width a cell can occupy in the design is called as ___.
a. Unit Tile cell
b. Multi
heighten cell
c.
LVT cell
d.
HVT cell
a. Cell Convergence Pessimism Removal
b. Cell Convergence Preset Removal
c. Clock Convergence Pessimism Removal
d. Clock Convergence Preset Removal
- 18) In OCV timing check, for setup time, ___.
a. Max delay is used for launch path and Min
delay for capture path
b. Min delay is used for launch path and Max
delay for capture path
c. Both Max
delay is used for launch and Capture path
d. Both Min
delay is used for both Capture and
Launch paths
- 19) "Total metal area and(or) perimeter of conducting layer / gate to gate area" is called ___.
a. Utilization
b. Aspect Ratio
c.
OCV
d. Antenna Ratio
- 20) The Solution for Antenna effect is ___.
a. Diode insertion
b. Shielding
c. Buffer insertion
d. Double spacing
- 21) To avoid cross talk, the shielded net is usually connected to ___.
a.
VDD
b.
VSS
c. Both
VDD and
VSS
d. Clock
- 22) If the data is faster than the clock in Reg to Reg path ___ violation may come.
a. Setup
b. Hold
c. Both
d. None
- 23) Hold violations are preferred to fix ___.
a.
Before placement
b. After placement
c. Before
CTS
d.
After CTS
- 24) Which of the following is not present in SDC ___?
a. Max
tran
b. Max cap
c. Max
fanout
d. Max current density
- 25) Timing sanity check means (with respect to PD)___.
a. Checking timing of routed design with out net delays
b. Checking Timing of placed design with net delays
c. Checking Timing of unplaced design without net delays
d. Checking Timing of routed design with net delays
- 26) Which of the following is having highest priority at final stage (post routed) of the design ___?
a. Setup violation
b. Hold violation
c. Skew
d. None
- 27) Which of the following is best suited for CTS?
a.
CLKBUF
b.
BUF
c.
INV
d.
CLKINV
- 28) Max voltage drop will be there at(with out macros) ___.
a. Left and Right sides
b. Bottom and Top sides
c. Middle
d. None
- 29) Which of the following is preferred while placing macros ___?
a. Macros placed center of the die
b. Macros placed left and right side of die
c. Macros placed bottom and top sides of die
d. Macros placed based on
connectivity of the I/O
- 30) Routing congestion can be avoided by ___.
a. placing cells closer
b. Placing cells at corners
c. Distributing cells
d. None
- 31) Pitch of the wire is ___.
a. Min width
b. Min spacing
c. Min width - min spacing
d. Min width + min spacing
- 32) In Physical Design following step is not there ___.
a.
Floorplaning
b. Placement
c. Design Synthesis
d.
CTS
- 33) In technology file if 7 metals are there then which metals you will use for power?
a. Metal1 and metal2
b. Metal3 and metal4
c. Metal5 and metal6
d. Metal6 and metal7
- 34) If metal6 and metal7 are used for the power in 7 metal layer process design then which metals you will use for clock ?
a. Metal1 and metal2
b. Metal3 and metal4
c. Metal4 and metal5
d. Metal6 and metal7
- 35) In a reg to reg timing path Tclocktoq delay is 0.5ns and TCombo delay is 5ns and Tsetup is 0.5ns then the clock period should be ___.
a. 1
ns
b. 3
ns
c. 5
ns
d. 6
ns
- 36) Difference between Clock buff/inverters and normal buff/inverters is __.
a. Clock buff/inverters are faster than normal buff/inverters
b. Clock buff/inverters are slower than normal buff/inverters
c. Clock buff/inverters are having equal rise and fall times with high drive strengths compare to normal buff/inverters
d. Normal buff/inverters are having equal rise and fall times with high drive strengths compare to Clock buff/inverters.
- 37) Which configuration is more preferred during floorplaning ?
a. Double back with flipped rows
b. Double back with non flipped rows
c. With channel spacing between rows and no double back
d. With channel spacing between rows and double back
- 38) What is the effect of high drive strength buffer when added in long net ?
a. Delay on the net increases
b. Capacitance on the net increases
c. Delay on the net decreases
d. Resistance on the net increases.
- 39) Delay of a cell depends on which factors ?
a. Output transition and input load
b. Input transition and Output load
c. Input
transition and Output
transition
d. Input load and Output Load.
- 40) After the final routing the violations in the design ___.
a. There can be no setup, no hold violations
b. There can be only setup violation but no hold
c. There can be only hold violation not Setup violation
d. There can be both violations.
- 41) Utilisation of the chip after placement optimisation will be ___.
a. Constant
b. Decrease
c. Increase
d. None of the above
- 42) What is routing congestion in the design?
a. Ratio of required routing tracks to available routing tracks
b. Ratio of available routing tracks to required routing tracks
c. Depends on the routing layers available
d. None of the above
- 43) What are preroutes in your design?
a. Power routing
b. Signal routing
c. Power and Signal routing
d. None of the above.
- 44) Clock tree doesn't contain following cell ___.
a. Clock buffer
b. Clock Inverter
c.
AOI cell
d. None of the above
1)b
2)c
3)b
4)c
5)b
6)d
7)a
8)c
9)d
10)b
11)d
12)d
13)b
14)c
15)b
16)a
17)c
18)a
19)d
20)a
21)b
22)b
23)d
24)d
25)c
26)b
27)a
28)c
29)d
30)c
31)d
32)c
33)d
34)c
35)d
36)c
37)a
38)c
39)b
40)d
41)c
42)a
43)a
44)c